EKS Anywhere Architecture
EKS Anywhere supports many different types of infrastructure including VMWare vSphere, bare metal, Nutanix, Apache CloudStack, and AWS Snow. EKS Anywhere is built on the Kubernetes sub-project called Cluster API (CAPI), which is focused on providing declarative APIs and tooling to simplify the provisioning, upgrading, and operating of multiple Kubernetes clusters. EKS Anywhere inherits many of the same architectural patterns and concepts that exist in CAPI. Reference the CAPI documentation to learn more about the core CAPI concepts.
Components
Each EKS Anywhere version includes all components required to create and manage EKS Anywhere clusters.
Administrative / CLI components
Responsible for lifecycle operations of management or standalone clusters, building images, and collecting support diagnostics. Admin / CLI components run on Admin machines or image building machines.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| eksctl CLI | Command-line tool to create, upgrade, and delete management, standalone, and optionally workload clusters. |
| image-builder | Command-line tool to build Ubuntu and RHEL node images |
| diagnostics collector | Command-line tool to produce support diagnostics bundle |
Management components
Responsible for infrastructure and cluster lifecycle management (create, update, upgrade, scale, delete). Management components run on standalone or management clusters.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| CAPI controller | Controller that manages core Cluster API objects such as Cluster, Machine, MachineHealthCheck etc. |
| EKS Anywhere lifecycle controller | Controller that manages EKS Anywhere objects such as EKS Anywhere Clusters, EKS-A Releases, FluxConfig, GitOpsConfig, AwsIamConfig, OidcConfig |
| Curated Packages controller | Controller that manages EKS Anywhere Curated Package objects |
| Kubeadm controller | Controller that manages Kubernetes control plane objects |
| Etcdadm controller | Controller that manages etcd objects |
| Provider-specific controllers | Controller that interacts with infrastructure provider (vSphere, bare metal etc.) and manages the infrastructure objects |
| EKS Anywhere CRDs | Custom Resource Definitions that EKS Anywhere uses to define and control infrastructure, machines, clusters, and other objects |
Cluster components
Components that make up a Kubernetes cluster where applications run. Cluster components run on standalone, management, and workload clusters.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | Kubernetes components that include kube-apiserver, kube-controller-manager, kube-scheduler, kubelet, kubectl |
| etcd | Etcd database used for Kubernetes control plane datastore |
| Cilium | Container Networking Interface (CNI) |
| CoreDNS | In-cluster DNS |
| kube-proxy | Network proxy that runs on each node |
| containerd | Container runtime |
| kube-vip | Load balancer that runs on control plane to balance control plane IPs |
Deployment Architectures
EKS Anywhere supports two deployment architectures:
-
Standalone clusters: If you are only running a single EKS Anywhere cluster, you can deploy a standalone cluster. This deployment type runs the EKS Anywhere management components on the same cluster that runs workloads. Standalone clusters must be managed with the
eksctlCLI. A standalone cluster is effectively a management cluster, but in this deployment type, only manages itself. -
Management cluster with separate workload clusters: If you plan to deploy multiple EKS Anywhere clusters, it’s recommended to deploy a management cluster with separate workload clusters. With this deployment type, the EKS Anywhere management components are only run on the management cluster, and the management cluster can be used to perform cluster lifecycle operations on a fleet of workload clusters. The management cluster must be managed with the
eksctlCLI, whereas workload clusters can be managed with theeksctlCLI or with Kubernetes API-compatible clients such askubectl, GitOps, or Terraform.
If you use the management cluster architecture, the management cluster must run on the same infrastructure provider as your workload clusters. For example, if you run your management cluster on vSphere, your workload clusters must also run on vSphere. If you run your management cluster on bare metal, your workload cluster must run on bare metal. Similarly, all nodes in workload clusters must run on the same infrastructure provider. You cannot have control plane nodes on vSphere, and worker nodes on bare metal.
Both deployment architectures can run entirely disconnected from the internet and AWS Cloud. For information on deploying EKS Anywhere in airgapped environments, reference the Airgapped Installation page.
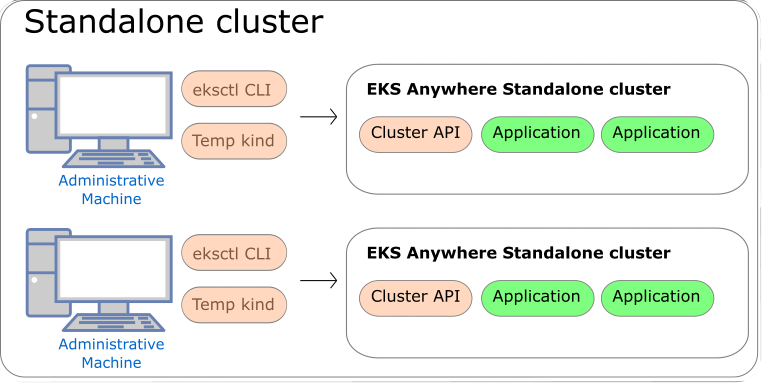
Standalone Clusters
Technically, standalone clusters are the same as management clusters, with the only difference being that standalone clusters are only capable of managing themselves. Regardless of the deployment architecture you choose, you always start by creating a standalone cluster from an Admin machine. When you first create a standalone cluster, a temporary Kind bootstrap cluster is used on your Admin machine to pull down the required components and bootstrap your standalone cluster on the infrastructure of your choice.
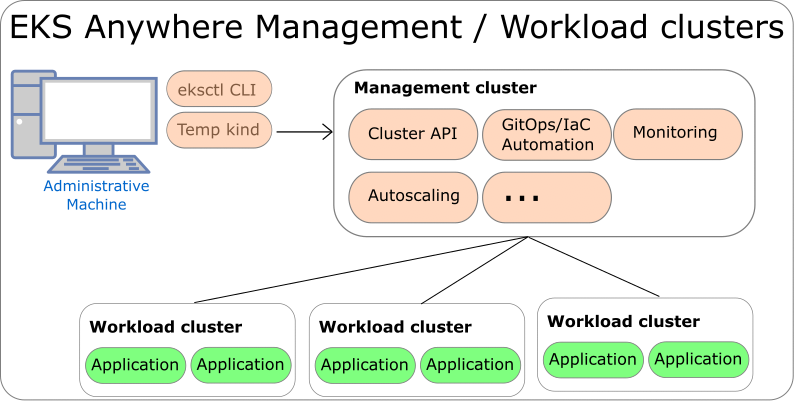
Management Clusters
Management clusters are long-lived EKS Anywhere clusters that can create and manage a fleet of EKS Anywhere workload clusters. Management clusters run both management and cluster components. Workload clusters run cluster components only and are where your applications run. Management clusters enable you to centrally manage your workload clusters with Kubernetes API-compatible clients such as kubectl, GitOps, or Terraform, and prevent management components from interfering with the resource usage of your applications running on workload clusters.